Given the roots of two binary trees root and subRoot, return true if there is a subtree of root with the same structure and node values of subRoot and false otherwise.
A subtree of a binary tree tree is a tree that consists of a node in tree and all of this node's descendants. The tree tree could also be considered as a subtree of itself.
Example 1:
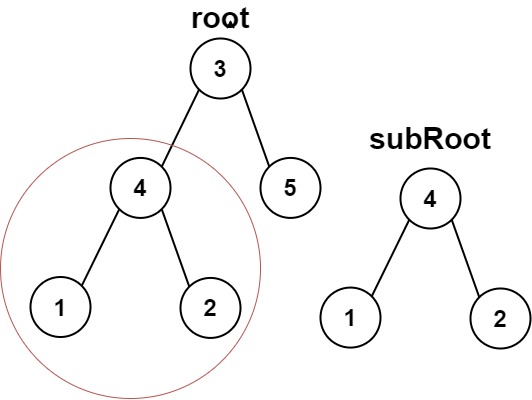
Input: root = [3,4,5,1,2], subRoot = [4,1,2]
Output: true
Example 2:
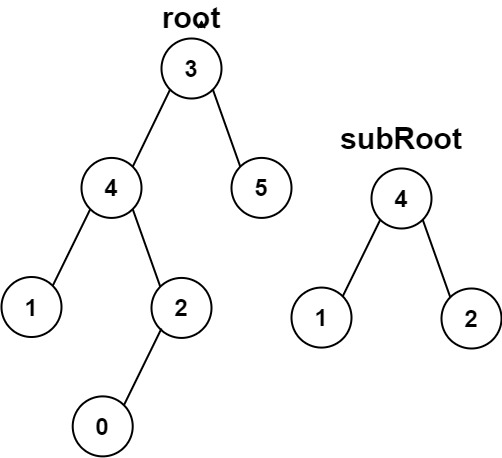
Input: root = [3,4,5,1,2,null,null,null,null,0], subRoot = [4,1,2]
Output: false
1) Explain the problem
We need to determine if one binary tree (subRoot) is a subtree of another binary tree (root). A subtree is a part of the tree consisting of a node and all its descendants. The subtree should have the same structure and node values as the specified subtree.
2) Short easy to remember solution/approach
Use a depth-first search (DFS) approach to traverse the main tree (root). At each node, check if the subtree starting from that node is identical to subRoot. Use a helper function to compare the two trees.
3) Solution in Javascript with code commenting
class TreeNode {
constructor(val, left = null, right = null) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
function isSubtree(root, subRoot) {
if (!root) return false;
if (isSameTree(root, subRoot)) return true;
return isSubtree(root.left, subRoot) || isSubtree(root.right, subRoot);
}
function isSameTree(p, q) {
if (p === null && q === null) return true;
if (p === null || q === null || p.val !== q.val) return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
// Example usage:
let root = new TreeNode(3);
root.left = new TreeNode(4);
root.right = new TreeNode(5);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(1);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(2);
let subRoot = new TreeNode(4);
subRoot.left = new TreeNode(1);
subRoot.right = new TreeNode(2);
console.log(isSubtree(root, subRoot)); // Output: true
4) Explanation of the solution in an easy-to-understand way. Explain it like a 10-year-old.
Imagine you have a big LEGO tree and a smaller LEGO tree. You want to check if you can find the exact same smaller tree inside the big tree. You start looking at each part of the big tree. If you find a part that looks exactly like the smaller tree, then you have found a match.
5) Code explanation in pointers
Define a
TreeNodeclass to represent each node in the tree.Create an
isSubtreefunction that:Returns
falseifrootisnull.Returns
trueif the trees starting fromrootandsubRootare the same.Recursively checks the left and right subtrees of
rootfor a match.
Define a helper function
isSameTreeto:Return
trueif both nodes arenull.Return
falseif one node isnullor their values differ.Recursively compare the left and right subtrees of both nodes.
Use the
isSubtreefunction to check ifsubRootis a subtree ofroot.
6) Complexities
Time Complexity: (O(m \times n)) - For each node in
root(n nodes), we may check if the subtree starting from that node matchessubRoot(m nodes).Space Complexity: (O(h)) - Where (h) is the height of the
roottree. This is due to the recursion stack.
